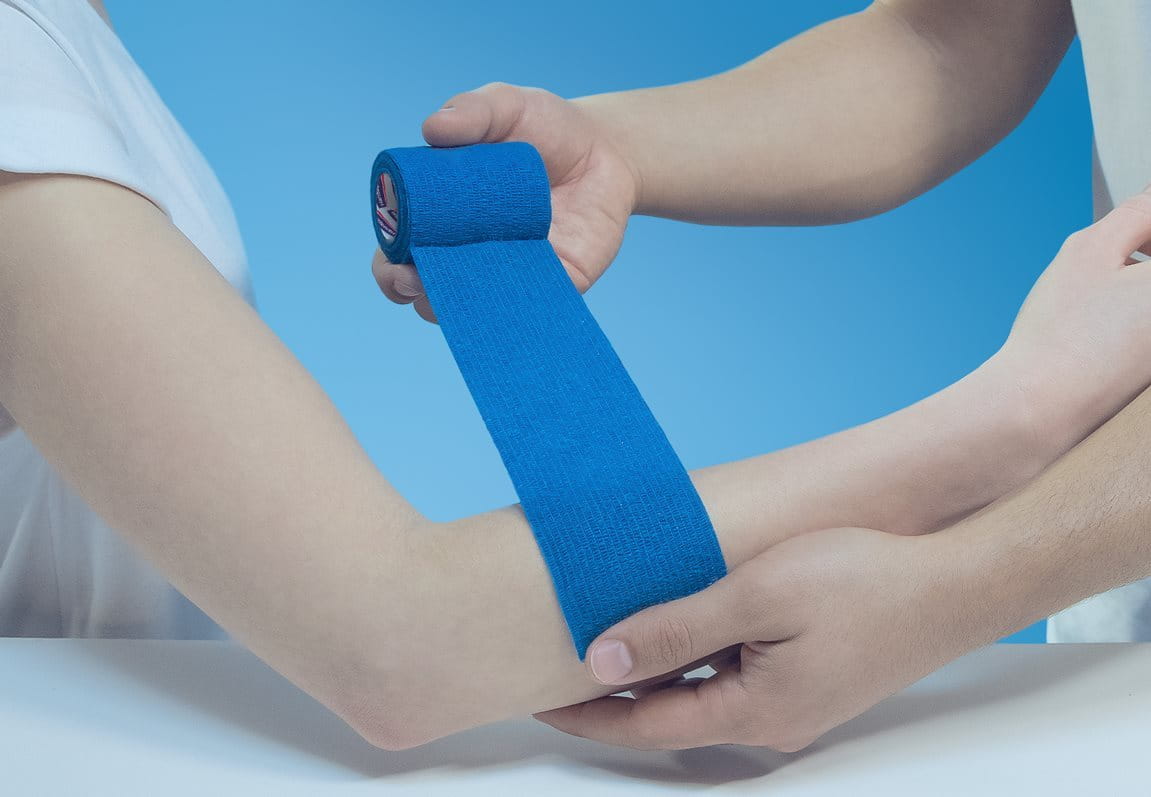
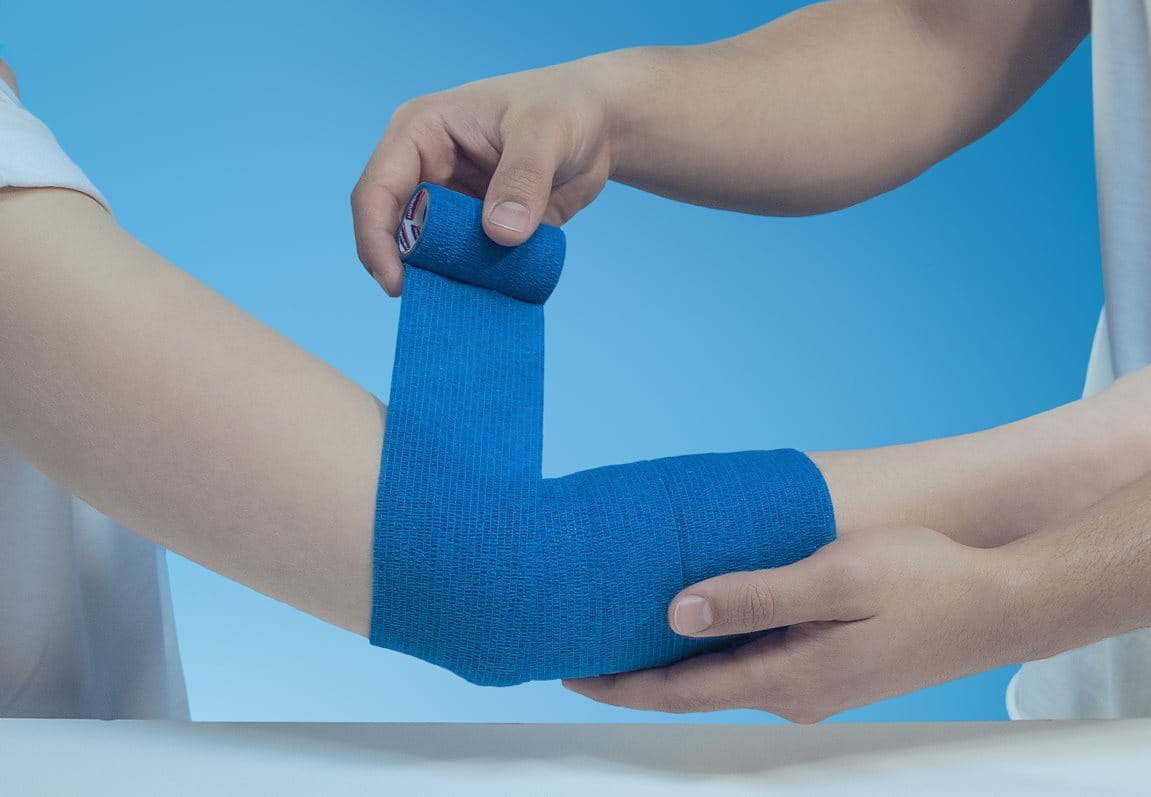
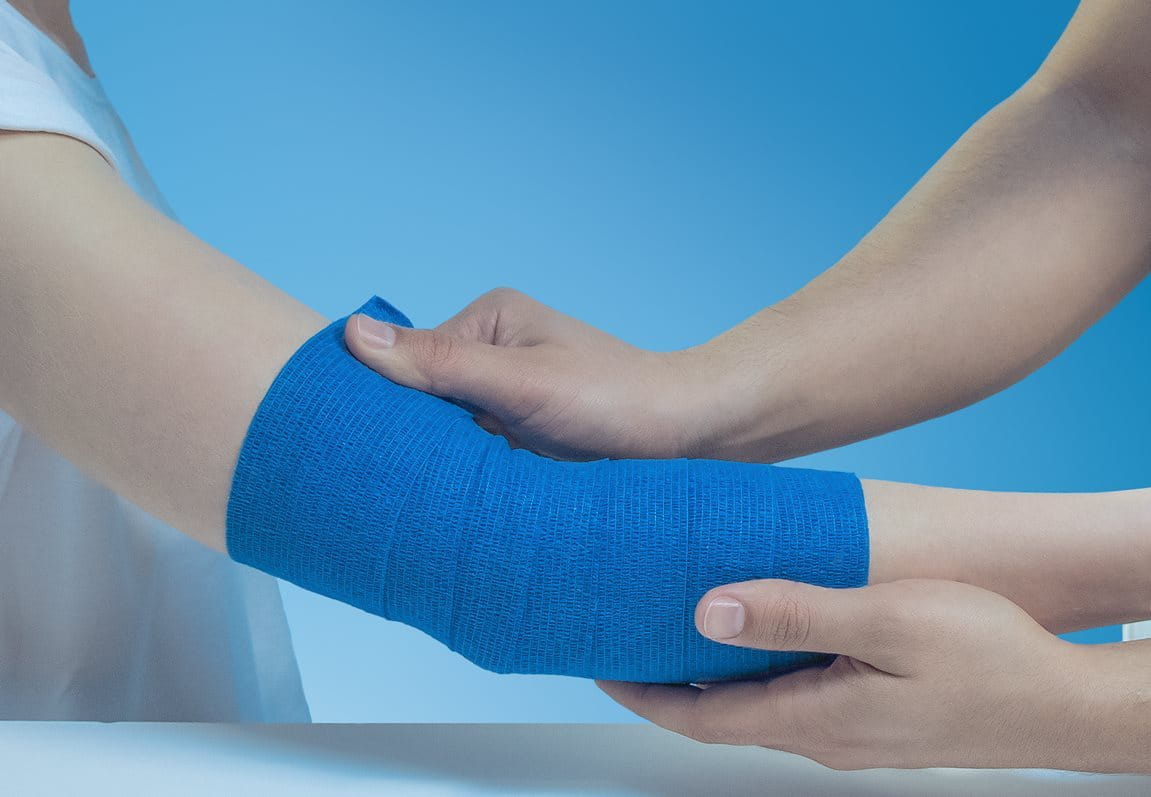
Self-adhesive, flexible and comfortable
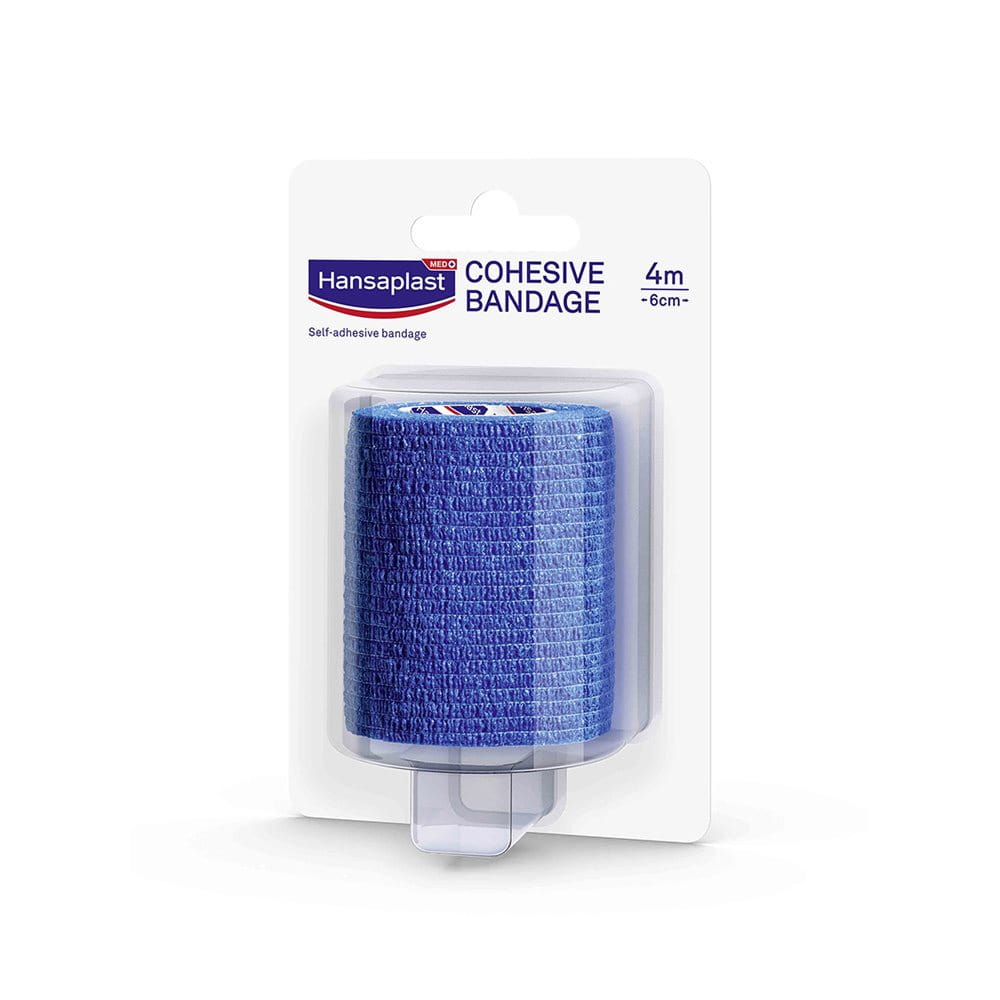
Cohesive Bandage Blue 4m x 6cm
Product Info
Hansaplast Cohesive Bandage
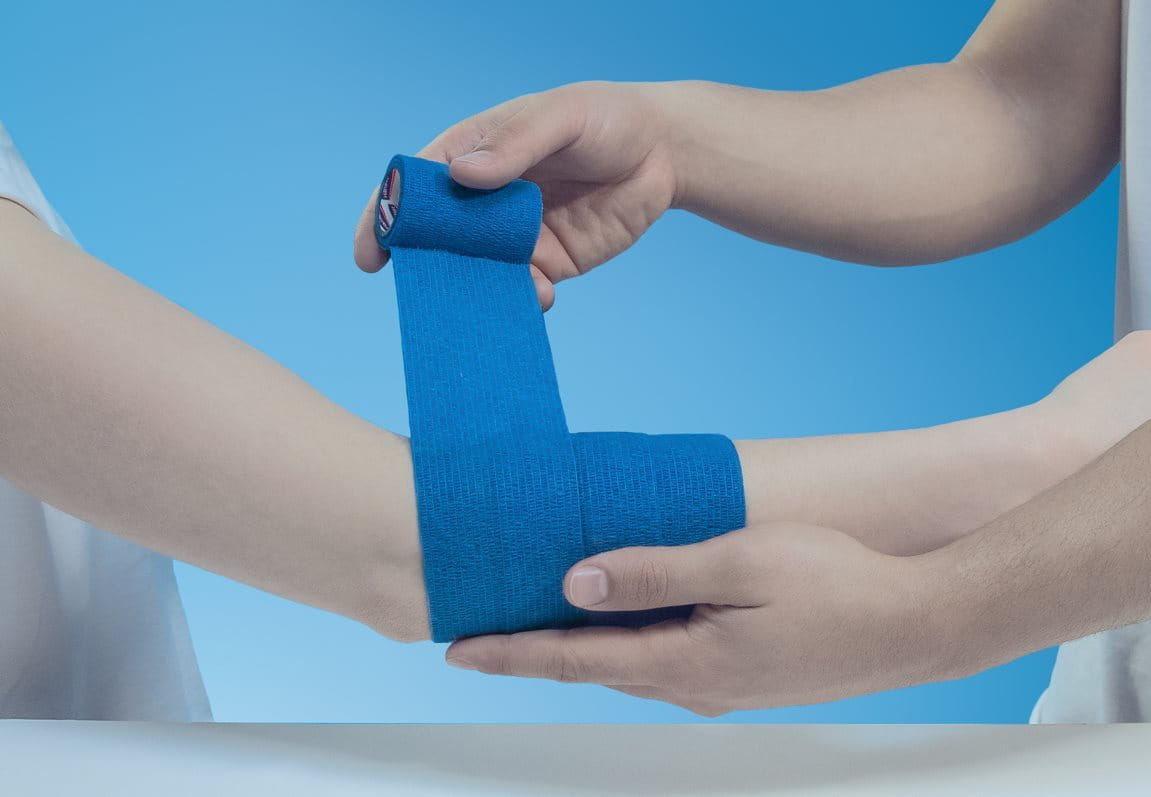
This self-adhesive and multipurpose bandage is designed to firmly secure wound dressings and compresses. Extra flexible and comfortable to wear, it can also be used for the support of joints.
The Hansaplast Cohesive Bandage is easy to use at home. It is hand-tearable and sticks to itself. The bandage itself provides secure adhesion, even in case of perspiration, and is resistant to water. It stays firmly in place without slipping.
Providing compression, elasticity and support, the Hansaplast Cohesive Bandage is free of latex and extra skin-friendly. It removes from the skin painlessly and leaves no adhesive residue behind.
How To Use
-
1. How often should I change the bandage?
For wound treatment the bandage is used for fixation of a wound pad or dressing. Usually, it is recommended to change the wound dressing daily for hygiene reasons. -
2. How do I apply the cohesive bandage?
Please find our detailed application advice in the Application tab. -
3. Is it better to let small wounds dry in the fresh air instead of putting on a bandage?
It is one of the wound care myths that keeping minor cuts and grazes uncovered and exposed to air helps them to heal faster. The contrary is true! Research shows that covered wounds heal more efficiently and have a reduced risk of infection. Hansaplast products provide protection until the wound is completely healed. -
4. When should I consult a doctor?
We recommend contacting a medical professional under the following circumstances:
- if the wound is deep and causing major bleeding
- if the wound shows signs of infection such as redness, warmth, pain and swelling
- if there are embedded foreign objects in it
- in case of animal or human bites
- if the wound is in the area of the face
- if there is insufficient tetanus vaccination
- and of course always when you have questions or are uncertain.
-
5. What if my wound gets infected and suppurates?
You should contact a medical professional if you recognize signs of infection. This is not only the occurrence of pus but also swelling, redness, heat, pain, itching or burning. In case of infection the wound will need medical care and special medical treatment. -
6. Why do I have to place an extra pad or dressing under the bandage when I have a wound?
The cohesive bandage does not contain a wound pad which is necessary to absorb blood and wound exudate and to ensure that the wound area is cushioned and hygienically protected. Thus, a wound should first be covered with a wound pad or dressing which then can be fixed with the cohesive bandage. -
7. How can I cushion the wounds?
You can use Hansaplast sterile compress to cushion your wounds. Sterile compresses like this are recommended by WHO and Red Cross for home first aid kits. This sterile compress made of soft and pure cotton protects large wounds such as cuts, grazes, burns, and lacerations.
-
8. What are the most common sports injuries?
Strains
A strain to the muscle or tendon can happen when the muscle is over stretched or excessively worked. This can cause the muscle to swell or fibres to rupture as in a torn hamstring. It may be painful and difficult to move or walk. Strains usually take one to six weeks to heal.
Bruises
A direct blow to the muscle tissue can result in bruising.
Tendonitis (inflammation of the tendon)
This can happen after excessive overuse. Often this is due to poor equipment or preparation, such as in tennis elbow.
Dislocation
This happens when a joint is injured and one or more bones are displaced from their normal position such as a dislocated finger or shoulder.
Sprains
This is an injury to a ligament and is caused by a sudden overstretching such as in a sprained ankle. It may be painful and difficult to move or walk. -
9. When should I consult a doctor?
Consult a health professional in case of any injury, or if you suspect joint strain or a medical condition like a fracture. A physician should be consulted in acute cases when these conditions are accompanied by reddening, swelling or hyperthermia of joints, persisting joint trouble or severe pain and/or are associated with neurological symptoms (e.g. numbness, tingling, loss of motion).
You should contact your doctor if symptoms persist. Please note that none of the given tips or recommendations substitute medical advice.